Do you wake up tired even after a full night’s sleep? Or does your partner notice pauses in your breathing at night? These could be signs of sleep apnea—a serious condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. Left untreated, it can raise the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke.
In this guide, we’ll explain:
What sleep apnea is and its main causes
The difference between a CPAP machine and a BiPAP machine
When oxygen therapy or a BiPAP ventilator is needed
Key symptoms and dangers to watch for
Sleep Apnea Explained
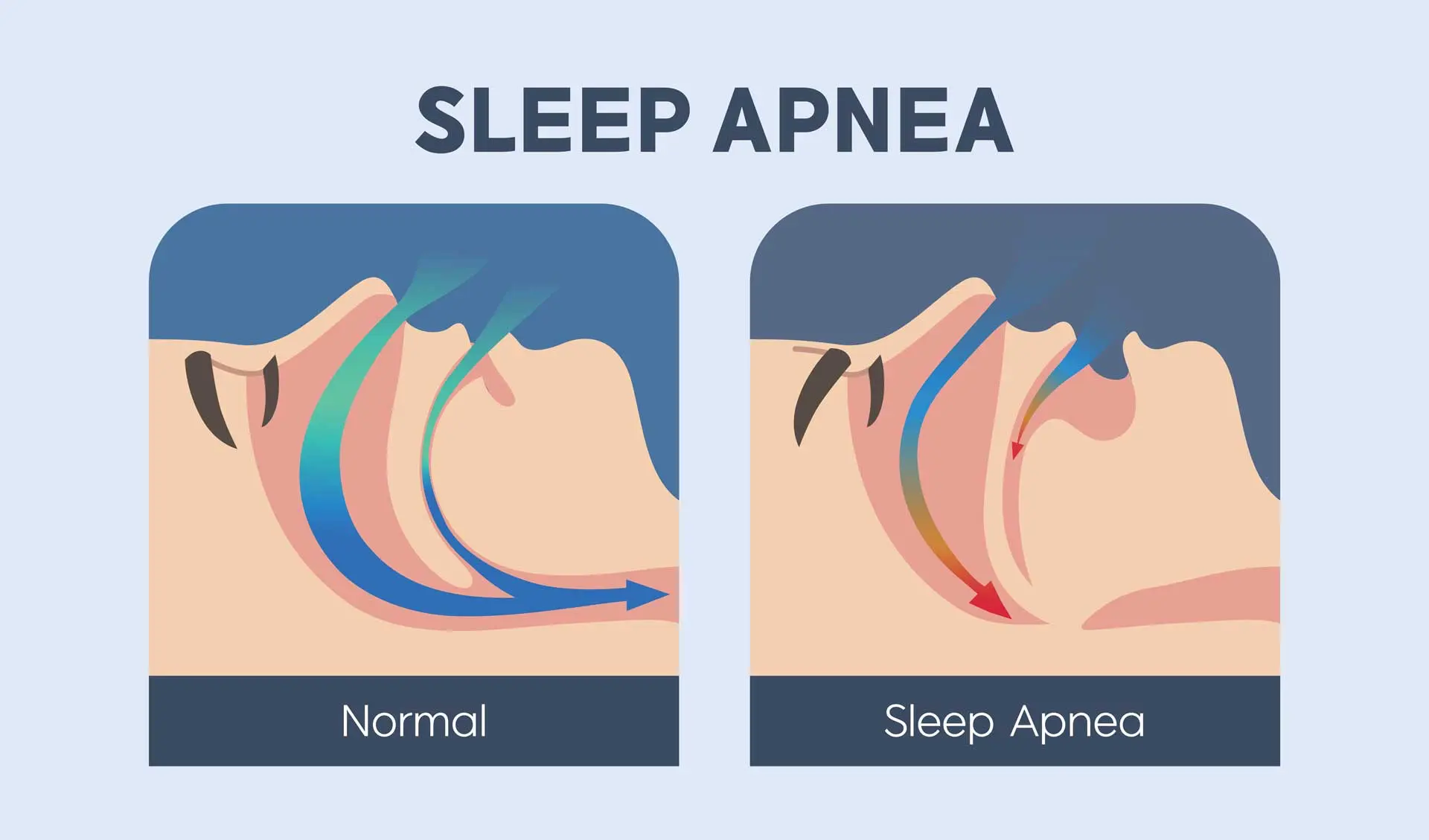
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder where the airway becomes blocked (obstructive sleep apnea) or the brain fails to send breathing signals (central sleep apnea). Both lead to disrupted sleep and low oxygen levels.
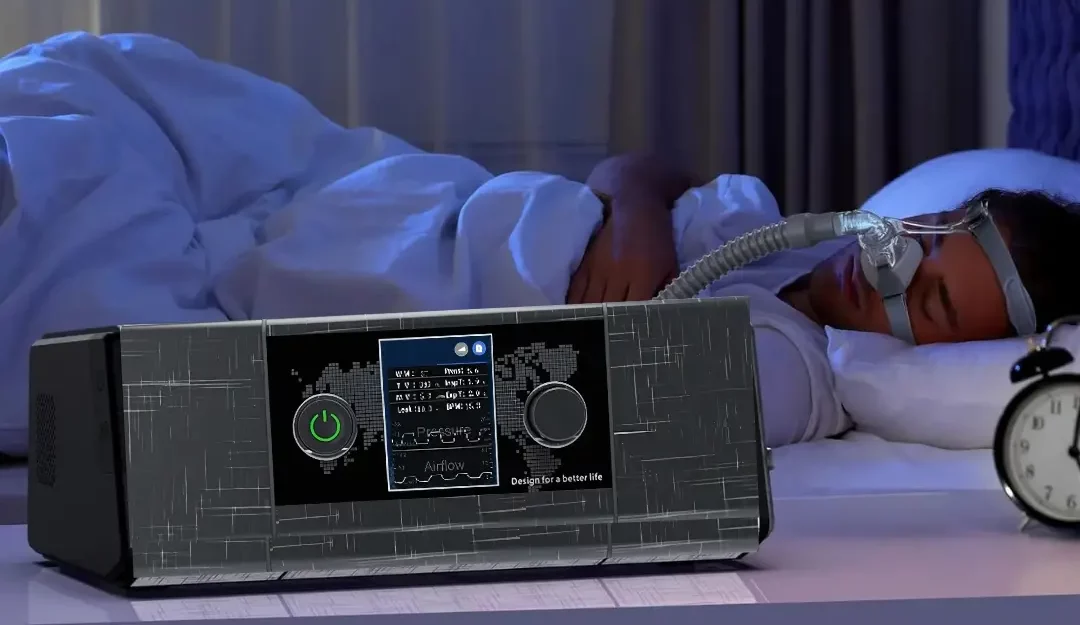
The standard treatment is positive airway pressure (PAP) therapy using a CPAP breathing machine or BiPAP device.
CPAP vs BiPAP: Key Differences
CPAP Machine (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure):
Delivers one constant stream of air to keep your airway open. Best for mild to moderate sleep apnea.
BiPAP Machine (Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure):
Provides two levels of pressure—higher when you inhale, lower when you exhale. Easier for people with severe sleep apnea, breathing difficulties, or other lung conditions.
BiPAP Ventilator:
Used in hospitals or at home for patients who need more advanced breathing support.
👉 For example, Broxtal’s Smart Auto BiPAP Machine VM-8 is designed to manage complex sleep apnea with comfort and flexibility.
Benefits of CPAP and BiPAP Therapy
Restores normal breathing at night
Improves sleep quality
Reduces daytime fatigue
Lowers risk of heart problems
Supports oxygen therapy for those with low oxygen saturation
Looking for a compact solution? Explore our Portable Oxygen Concentrators, ideal for patients needing extra oxygen on the go.
Causes of Sleep Apnea
The main causes of sleep apnea include:
Excess weight or obesity
Relaxed throat muscles during sleep
Narrow airway or enlarged tonsils
Genetic factors
Neurological issues (in central sleep apnea)
FAQs About Sleep Apnea
What is the main cause of sleep apnea?
The main cause is airway blockage due to relaxed throat muscles, often worsened by obesity or anatomical factors.
What are the dangers of sleep apnea?
Untreated sleep apnea can lead to:
- High blood pressure
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Type 2 diabetes
- Chronic fatigue and accidents
What are the warning signs of sleep apnea?
The most common signs include:
- Loud snoring
- Gasping or choking at night
- Morning headaches
- Dry mouth upon waking
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
What are 5 symptoms of sleep apnea?
- Loud snoring
- Pauses in breathing during sleep
- Waking up with a dry mouth
- Morning headaches
- Daytime fatigue or irritability
Can you recover from sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea often requires long-term management. Lifestyle changes such as weight loss, quitting smoking, and consistent use of a CPAP breathing machine can significantly reduce symptoms. In some cases, surgery may help.
What happens if sleep apnea is untreated?
Untreated sleep apnea increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, memory issues, and even shortened lifespan. It also worsens overall quality of life.
For medical guidance on sleep apnea and its treatments, see the Mayo Clinic’s overview on Sleep Apnea.
Taking Control of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is more than just snoring—it’s a health risk that demands attention. Understanding the differences between CPAP vs BiPAP machines helps you choose the right therapy.
At Broxtal, we provide advanced solutions, from CPAP breathing machines to BiPAP ventilators and portable oxygen therapy devices, so you can breathe and sleep better.
👉 Explore our full range of sleep therapy devices and take the first step toward healthier nights.
Explore More Guides on Sleep Apnea & Oxygen Therapy
Complete Guide to Oxygen Therapy Devices: Benefits & When to Use Them
From Snoring to Sleep Apnea: How Oxygen & Airway Devices Improve Breathing at Night
Oxygen Concentrator: What It Is, How It Helps, and What need to Know


